The working principle of axial piston motor is shown in Figure 2-23. The structure of axial piston motor is similar to that of axial piston pump, but considering the requirements of forward and reverse rotation, its structural arrangement (including the arrangement of oil distribution pan, oil groove and inlet and outlet oil passages) is symmetrical. Because the axial piston motor can easily realize variable displacement, it is also widely used.
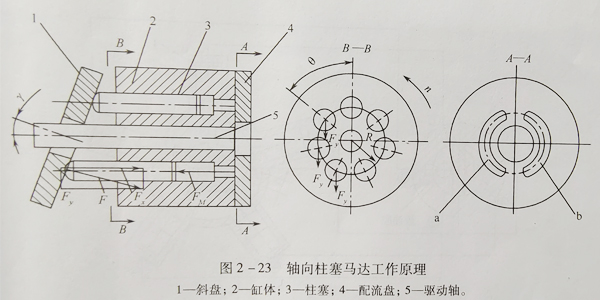
In the figure, swashplate 1 and port plate 4 are fixed, plunger 3 is in cylinder 2, drive shaft 5 is connected with cylinder 2 and can rotate together, and the center line of swashplate and cylinder intersect at an included angle γ。 When the pressure oil enters the plunger hole on the cylinder block connected with the window a through the port distribution window a on the port plate, the pressure oil pushes the plunger out and presses it on the swashplate. Due to the counter clockwise force of the rotating speed of the plunger and the normal force of the rotating surface of the right steering wheel F, the counter clockwise force of the rotating torque of the plunger is connected with the rotating force of the right steering wheel F, which is perpendicular to the rotating force of the plunger on the rotating surface of the cylinder block, and the force of the rotating torque of the right steering wheel f is connected with the rotating force of the plunger, At the same time, the plunger in the plunger hole communicated with the distribution window B is pressed back by the swashplate to discharge the oil in the plunger hole from the distribution window B. It must be pointed out that the hydraulic motor is used to drag the external load to do work. Only when the external load torque exists, the pressure oil entering the hydraulic motor can establish the corresponding pressure value, and the hydraulic motor can produce the corresponding torque to overcome it. Therefore, the torque of the hydraulic motor changes with the change of the external load torque.